Partition Magic - Partition Manager Software
Extend partition with one step
Resize/Move partition without data loss.
Create, delete and format partion with simple steps. Copy partition and disk to transfer data with ease. Support disk and partition size larger than 2 TB. Keep your data safe even in case of power outages or hardware failure.
Resize/Move partition without data loss.
Create, delete and format partion with simple steps. Copy partition and disk to transfer data with ease. Support disk and partition size larger than 2 TB. Keep your data safe even in case of power outages or hardware failure.

Glossary
-
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
A
Action Panel
The left tab of the PartitionMagic main screen, containing tasks, operations, and pending operations.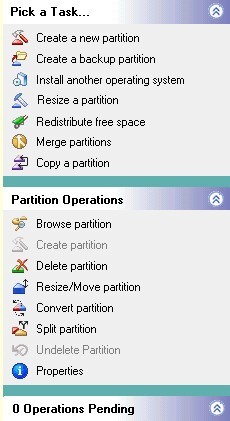
active partition
One primary partition (usually on the first hard disk) is marked "active," meaning it is the partition from which an operating system will be booted when the computer starts up.
ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
A department of the United States government responsible for approving U.S. standards in computers and communications. ANSI also works with the International Organization for Standards, or ISO.
ATA (Advanced Technology Attachment)
A standard used by hard-disk drives to communicate with the controller ports or cards, allowing the drive to interface with the computer. Before ATA, there were numerous incompatible methods for interfacing hard-disk drives to computers. ATA simplifies this process, thus reducing the cost of developing and purchasing related hardware. ATA is the official ANSI name for Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE).
ATA-2 (ATA Interface with Extensions)
ATA-2 is the common name for a new EIDE standard. Also dubbed "Fast ATA," ATA-2 extends the ATA interface while maintaining compatibility with current BIOS designs. The most noticeable result is increased speed. ATA-2 is still evolving and has not yet been approved as an official standard.
B
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
BIOS is a program code stored in ROM that provides the lowest-level access to peripheral devices and controls the first stage of a computer's boot process.
boot
To load and initialize an operating system on a computer.
bootable partition
A partition from which an operating system can be started.
BootMagic
A PowerQuest program that lets you choose the active operating system partition when you start or reboot your system.
boot record
See master boot record and partition boot record.
boot sector
The first sector of a hard-disk partition. If the partition is bootable, the boot sector contains a boot record, which is code used to boot the operating system installed on that partition.
byte
One byte is equal to 8 bits of information.
C
CHS
Cylinder, head, sector. A three-dimensional address of a hard-disk sector.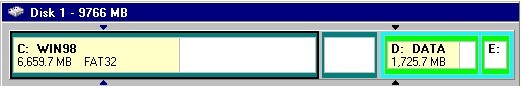
cluster
The smallest allocation unit in the FAT, FAT32, and NTFS file systems. One cluster consists of a fixed number of disk sectors.
cylinder
The set of all tracks, one on each side of each platter of a hard disk, that are located at the same distance from the center of a hard disk.
D
disk map
The section of the PartitionMagic main window that graphically displays a selected hard disk's partition information. The disk map, pictured below, shows the partitions approximately to scale. Each partition is represented by a different color according to the file system it uses. If the hard disk contains logical partitions, the logical partitions are shown within an extended partition.
DOS
An acronym for Disk Operating System, and is the name of a number of operating systems that include facilities for storing files on disk. It coordinates physical disk I/O, mapping of file names to disk addresses, and protection of files from unauthorized access. A DOS usually presents a uniform interface to different storage devices such as floppy disks, hard disks, magnetic tape drives, and CD-ROM drives. It may also provide file locking to prevent unintentional simultaneous access by two processes. A DOS also manages other computer resources such as memory, printers, and networks.
drive
1) Short for hard-disk drive. 2) Short for logical drive.
drive letter
A single character in the range A to Z that identifies a partition or logical drive for use by an operating system. Not all partitions or logical drives are accessible by all operating systems. Also, the drive letters assigned by different operating systems to the same partition or logical drive may not be the same.
DriveMapper
A PowerQuest tool that helps you easily update drive letter references. For example, if you create, delete, hide, or unhide a partition, your drive letters can change, causing applications not to run because application shortcuts, initialization files, and registry entries refer to incorrect drives. DriveMapper updates these drive letter references, allowing your applications to run correctly. DriveMapper also runs automatically under the following conditions: (1) you apply changes to your system that affect drive letter assignments, (2) you are running Windows 95 or Windows 98, (3) your hard disk contains only FAT or FAT32 partitions, and (4) you have no more than one CD-ROM drive and no more than one removable drive.
dual boot
A generic term referring to the ability to boot multiple operating systems from a single partition by replacing the boot sector code of the partition. This is also called "multi-boot."
E
EIDE (Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics)
A marketing program that promotes certain features of ATA-2.
EB
Exabyte (Ebyte, E-byte). One exabyte is equal to 1,024 petabytes or 1 quintillion bytes of information.
Extended partition
An extended partition is a special kind of primary partition that was developed to overcome the four partition limit. The extended partition is a container inside of which you can create logical partitions. The extended partition itself does not hold any data, nor is it assigned a drive letter. But logical partitions inside the extended partition can hold applications and data and are assigned drive letters.
EPBR (Extended Partition Boot Record)
The IBM/Microsoft implementation of logical partitions makes each logical partition resemble a physical hard disk. On this "logical" hard disk, an EPBR occupies the same position as the MBR of a physical hard disk. The EPBR may contain two entries. One is a logical partition, corresponding to a physical partition on a physical drive. The other may be an entry for another EPBR, corresponding to the extended partition on a physical drive.
F
FAT (File Allocation Table)
A file system developed for MS-DOS by Microsoft. The FAT file system is named after the file allocation table, one of the key architectural elements of the FAT file system. DOS, Windows 95/98/Me, Windows NT/2000/XP, and Linux can use partitions formatted with the FAT file system.
FAT32
A file system used by Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2, Windows 98/Me/2000/XP. FAT32 is an enhancement of the FAT file system and is based on 32-bit file allocation table entries, rather than the 16-bit entries used by the FAT system. As a result, FAT32 supports much larger disk or partition sizes (up to 2 terabytes).
File system
The method an operating system uses to organize files on a disk. Common file systems are FAT, FAT 32, NTFS, Linux Ext2, and Linux Swap.
format
1) v. To construct the framework on the partition necessary for a file system to name, store, and retrieve files. 2) n. An operating system command that formats a partition.
Free space
Unused space within a partition. Do not confuse free space with unallocated space, which resides outside a partition.
G
GB
Gigabyte. One gigabyte is equal to 1,024 megabytes or 1 billion bytes of information.
H
Head
A side of a hard-disk platter. More specifically, the hardware assembly that reads and writes data on a hard-disk platter.
hexadecimal
A system of numbers with base 16 that uses the 16 digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F. The letters A, B, C, D, E, and F correspond to the numbers 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
Hdden partition
A partition that is not assigned a drive letter by an operating system when it boots. A hidden partition is invisible to the operating system and all connected applications; therefore, data on a hidden partition cannot be accessed.
I
IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics)
See ATA.
J
K
KB
Kilobyte. One kilobyte is equal to 1,024 bytes. A kilobyte is also a unit of measurement for computer file sizes.
L
Label
The name that you give to a volume or partition.
LBA (Logical Block Addressing)
1) In EIDE, a means of specifying sector addresses by replacing CHS values with a single linear 28-bit number. 2) Generically, a one-dimensional address of a hard-disk sector; contrast with CHS.
Linux
A freeware version of the UNIX operating system. It can access primary and logical partitions formatted with Linux Ext2 and Linux Swap.
Linux Ext2
A file system developed for Linux.
Linux Swap
A file system developed for Linux; used for the Linux swap file.
logical drive
1) A contiguous area inside an extended partition that can be used by the operating system to store and retrieve files. The operating system typically assigns a letter (for example, D:, E:) to the logical drive. In this help system, the term "logical partition" is used in place of "logical drive." 2) Any partition, CD-ROM, or other storage device that contains a file system and is assigned a drive letter.
logical partition
This help system uses the term "logical partition" in place of "logical drive" to refer to a partition inside an extended partition.
LFN (Long Filename)
Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP and other operating systems do not have to adhere to DOS's file naming system, in which a filename can have no more than eight characters and a three-character extension. Filenames that violate this DOS format are considered LFNs. LFNs can have as many as 254 characters. Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP use additional directory entries. See VFAT.
Lost clusters
Data areas on partitions that are not part of any file's cluster chain. Lost clusters can occur when the file system does not completely update the partition type due to a system failure or power failure.
M
MB
Megabyte. One megabyte is equal to 1,048,576 bytes (1,024 x 1,024).
MBR (Master Boot Record)
The master boot record is contained in the first sector of the first physical hard disk. The MBR consists of a master boot program and a partition table that describes the disk partitions. The master boot program looks at the partition table to see which primary partition is active. It then starts the boot program from the boot sector of the active partition.
multi-boot
See dual boot.
N
NTFS (New Technology File System)
A file system developed by Microsoft and accessible only through Windows NT/2000/XP. NTFS eliminates many of the shortcomings of the FAT file system, such as wasteful cluster sizes and a slow CHKDSK execution time.
O
operating system
An operating system allows programs to cooperatively use a computer's resources (for example, disks, memory, printers, and networks). Common operating systems are MS-DOS, Linux, and Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP.
P
partition
A contiguous area of a hard disk that the operating system can format with a file system. The term "partition" can refer to either a primary or logical partition.
partition boot record
The partition boot record is located in the first sector of a hard-disk partition. It contains code used to boot the operating system installed on that partition.
partition list
The section of the PartitionMagic main window that displays a selected hard disk's partition information in text form. The partition list, pictured below, displays the following information about each partition: drive letter, volume label, file system type, size, amount of used and free space, status, and whether the partition is a primary or logical partition.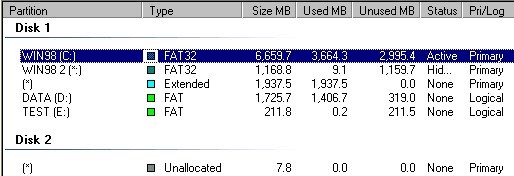
PB
Petabyte (Pbyte, P-byte). One petabyte is equal to 1,024 terabytes or 1 quadrillion bytes of information.
primary partition
A partition referenced in the master boot record (MBR) partition table. Only four primary partitions can exist on a hard disk. One of these may be an extended partition. Only one primary partition on a drive may be active at a time. When one primary partition is active, the other primary partitions are typically not accessible. Data and programs are often placed on a logical partition inside an extended partition. This enables the data to be accessed by all primary partitions.
Q
R
S
sector
The smallest addressable section on a disk. It is used to record one block of a program or data. Each head on each track is typically divided into 17 or more sectors.
T
TB
Terabyte (Tbyte, T-byte). One terabyte is equal to 1,024 gigabytes or 1 trillion bytes of information.
track
A circular path on a disk to which data can be written and from which data can be read.
U
unallocated space
A section of your hard disk that is not currently assigned to a partition. Unallocated space is not recognized by the operating system. Usually, you do not want unallocated space because that section of your hard disk will not be used. You can either resize a partition larger to incorporate unallocated space or create a new partition in the unallocated space. Do not confuse unallocated space, which resides outside any partition, with free space within a partition.
V
VFAT
VFAT is an extension to the FAT file system that adds support for long filenames. Although the term "VFAT" originated as the name of the Windows for Workgroups FAT file system driver, it has come to refer to the extensions to the FAT file system added by Windows NT 3.51 and Windows?5.
visible partition
A partition that is assigned a drive letter by an operating system when it boots. You can access files, applications, and other data from visible partitions.
volume
1) A partition that has been high-level formatted by a particular operating system; a logical partition. 2) A set of partitions handled by the operating system as if they were a single logical partition.
volume label
The name that you give to a partition or volume.
W
Windows 95
An operating system developed by Microsoft. Windows 95 is a descendant of DOS and Windows 3.x. It can access primary and logical partitions formatted with the FAT file system. It supports long filenames using the VFAT extension to FAT.
Windows 98
An operating system developed by Microsoft operating system that uses the FAT32 file system, allowing it to access primary and logical partitions larger than 2 GB and support filenames longer than 254 characters. Windows 98 can also access partitions formatted with FAT.
Windows Me
The newest Microsoft operating system for the home user and the upgrade from Windows 98.
Windows 2000
A Microsoft operating system for corporate network use and the upgrade from Windows NT 4.0. Windows 2000 uses NTFS (version 5.0) and can access FAT and FAT32 file systems.
Windows NT
An operating system developed by Microsoft. Windows NT can access primary and logical partitions formatted with FAT and NTFS.
Windows XP
The newest Microsoft operating system for corporate network and home use and the upgrade from Windows NT/2000, Windows Me, and Windows 98 SE. It features a 32-bit computing architecture that is built on the code base of Windows 2000 and Microsoft's other popular consumer operating systems. See the Microsoft website for more information about Windows XP Professional and Home Edition.
Partition Manager Help
Getting Started
- Before You Run PartitionMagic
- Hard Disk Integrity Checks
- PartitionMagic Interface
- Four Steps to Complete a Task
- Change preferences
- Partition Basics
- What is a Hard Disk?
- What is Disk Formatting?
- Understanding File Systems
- Understanding Partitions
- Understanding How a Computer Boots
- Managing Your Partitions
- Freeing Disk Space Before Enlarging a FAT Partition
- Understanding Hidden Partitions
- Understanding Drive Letters
- Understanding the BIOS 1024 Cylinder Limit
- Understanding the 2 GB Boot Code Boundary
- Changing the BIOS LBA Mode Setting
- Restoring System Files
How do I ……?
- General
- Apply Changes
- Undo last Change
- Discard All Changes
- Change preferences
- Password-protect Partition Magic
- Change a password
- Remove password Protection
- Exit PartitionMagic
- View
- Operations
- Hard Disk Integrity Checks
- Resize a partition
- Move a partition
- Copy a partition
- Create a partition
- Delete a partition
- Undelete a partition
- Change a partition label
- Format a partition
- Convert FAT to FAT32 or NTFS to FAT/FAT32
- Convert FAT/FAT32 to 4K aligned
- Convert FAT/FAT32 to NTFS
- Convert FAT32 to FAT
- Convert a partition to Primary/Logical
- Merge a partition
- Split a partition
- View partition information
- Check a partition for errors
- Use MS ScanDisk to check for errors
- Use Windows CheckDisk to check for errors (Windows NT/2000/XP only)
- View pending operations
- Advanced
- Retest bad sectors
- Hide a partition
- Resize the root directory
- Set the active partition
- Resize clusters
- Change a drive letter (NT only)
- Tools
- PQBoot
- Drive Mapper
- BootMagic Configuration
- Create Rescue Disks
- PartitionInfo and PARTINFO
- Tasks
- Use a task
- Create New MiniTool Partition Wizard
- Resize Partitions Wizard
- Redistribute Free Space Wizard
- Merge Partitions Wizard
- Copy Wizard
- Display/hide task buttons
- Install Another OS task
- Create Backup Partition task
- Scenarios
- Create Scenario: To create a logical partition on a secondary hard disk
- Create Scenario: To create a Linux logical partition
- Create Scenario: To create a primary partition for Windows NT
- Add free space to a logical partition
- Add free space to a primary partition
- User PartitionMagic with other software
About the Features
- Apply Changes
- Bad Sector Retest
- BootMagic Configuration
- Change Drive Letter
- Check for Errors
- Convert
- Copy
- Create
- Creating an Operating System Boot Disk
- Create Rescue Disk
- Delete
- Discard All Changes
- DriveMapper
- Exit
- File Browser
- Format
- Help
- Hide Patition
- Info
- Label
- Merge
- MS ScanDisk
- Operations Pending
- PartitionInfo
- PQBoot
- PQBoot for Windows
- Preferences
- Resize Clusters
- Resize/Move
- Resize Root
- Set Active
- Set Password
- Split
- Tasks
- Undelete
- Undo Last Change
- View Menu
- Windows CheckDisk
Troubleshooting
- Generay
- Freeing Memory to Run PartitionMagic
- Make the operating system assign a CD-ROM drive letter
- Use PartitionMagic with a SCSI hard disk
- PqRP Partitions
- Resolving Check Errors
- Resolve partition table errors
- Partition Tables and Viruses
- Additional Help
Technical Support
Glossary